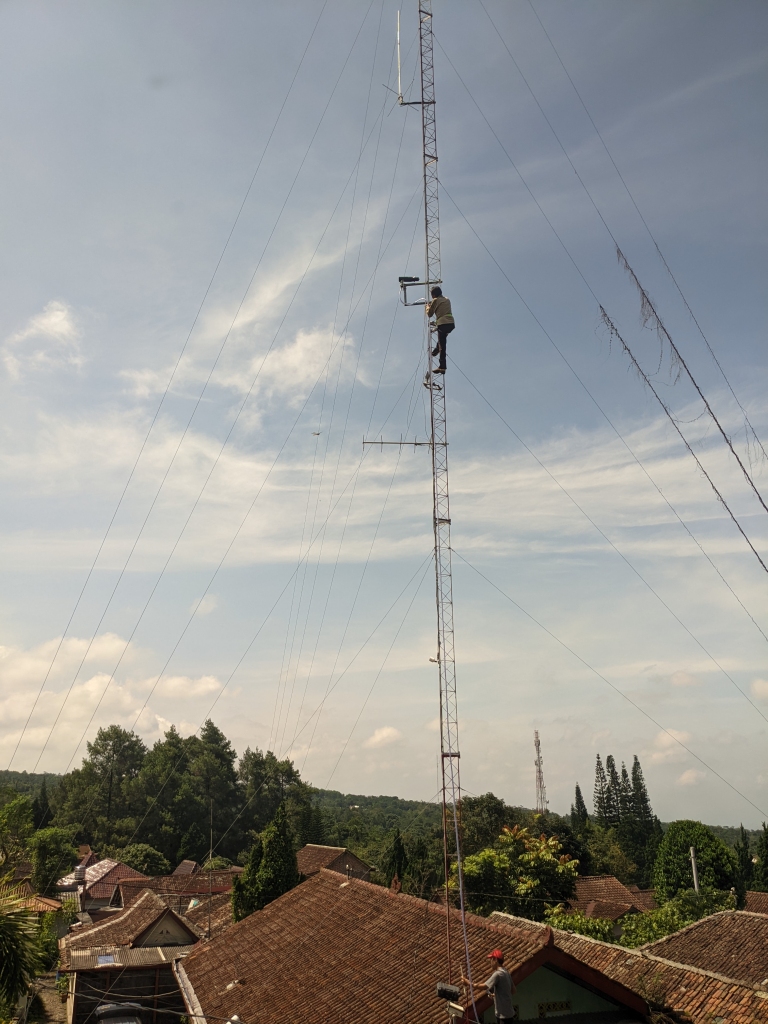
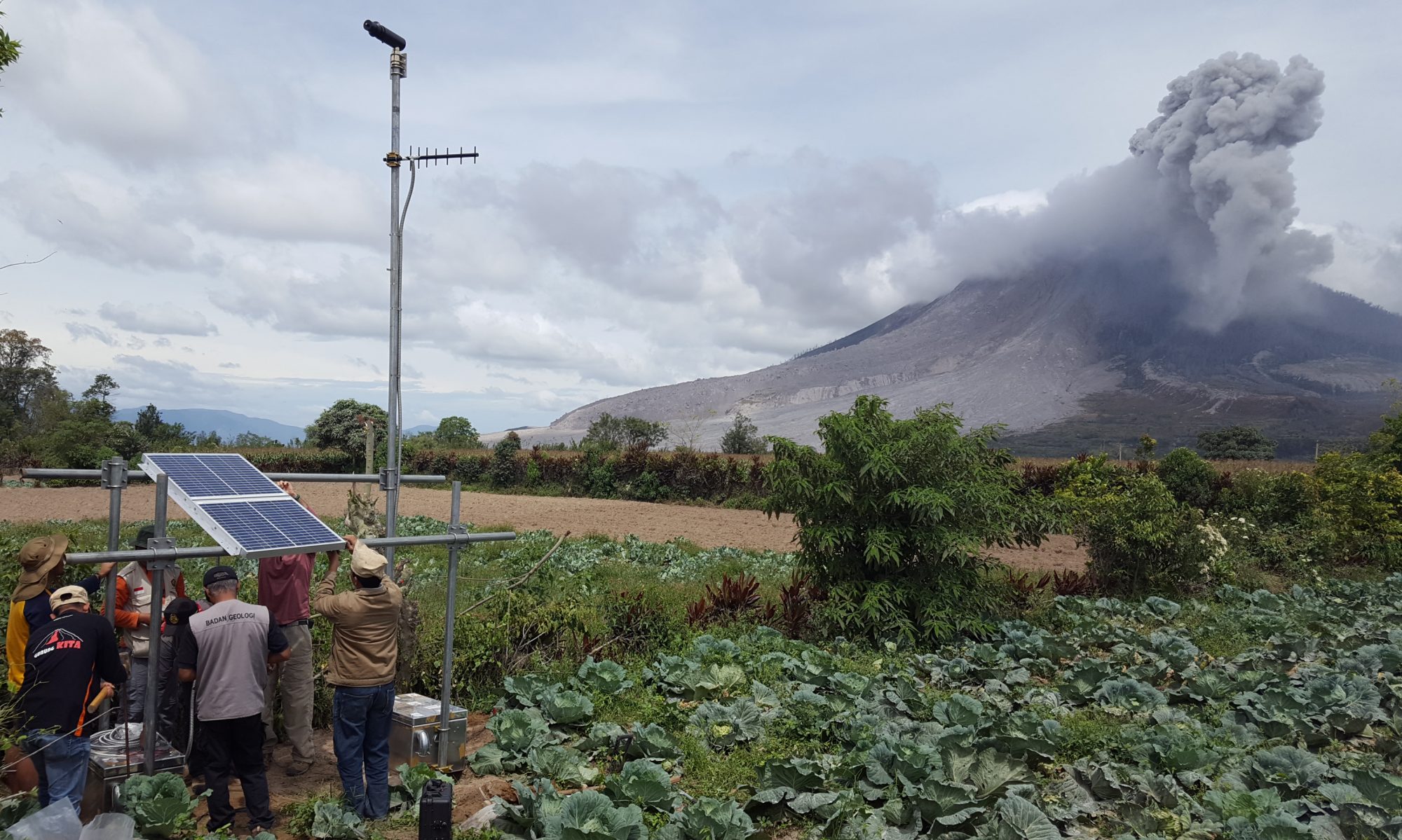
Merapi Volcano (Java, Indonesia) is a high-threat volcano with a history of eruptions that have had significant impact on tens of thousands of people living in the larger Yogyakarta metropolitan area. Merapi has been particularly active, erupting lava and producing pyroclastic flows, and the volcano’s alert level has been kept at the second highest mark (“Siaga”) since 2020. Supported by the USGS-USAID Volcano Disaster Assistance Program, gas geochemists and field engineers with the Indonesian Balai Penyelidikan dan Pengembangan Teknologi Kebencanaan Geologi (BPPTKG) have now installed a network of Scanning DOAS instruments on the volcano. Located at forward observation posts to the north, west, and south of the Merapi’s summit, the instruments allow SO2 emission rates to be tracked continuously and compared with other indicators of volcanic activity. The BPPTKG produced a short video describing the project, which can be viewed at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c8FmAJ-zCPk&t=1s