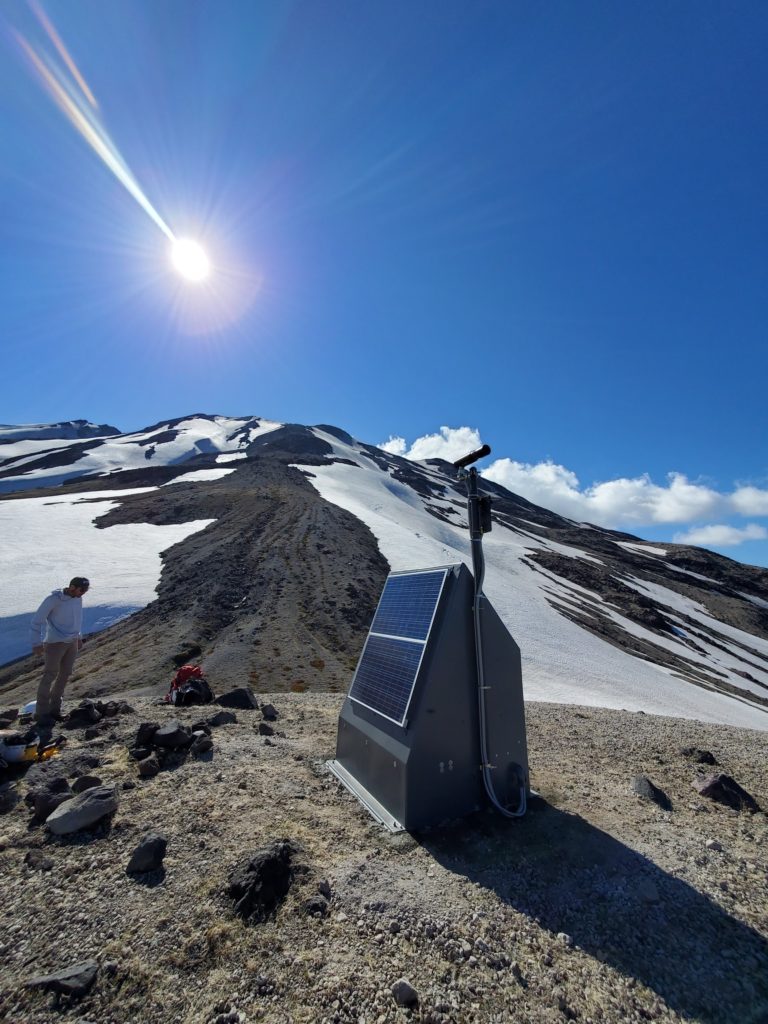
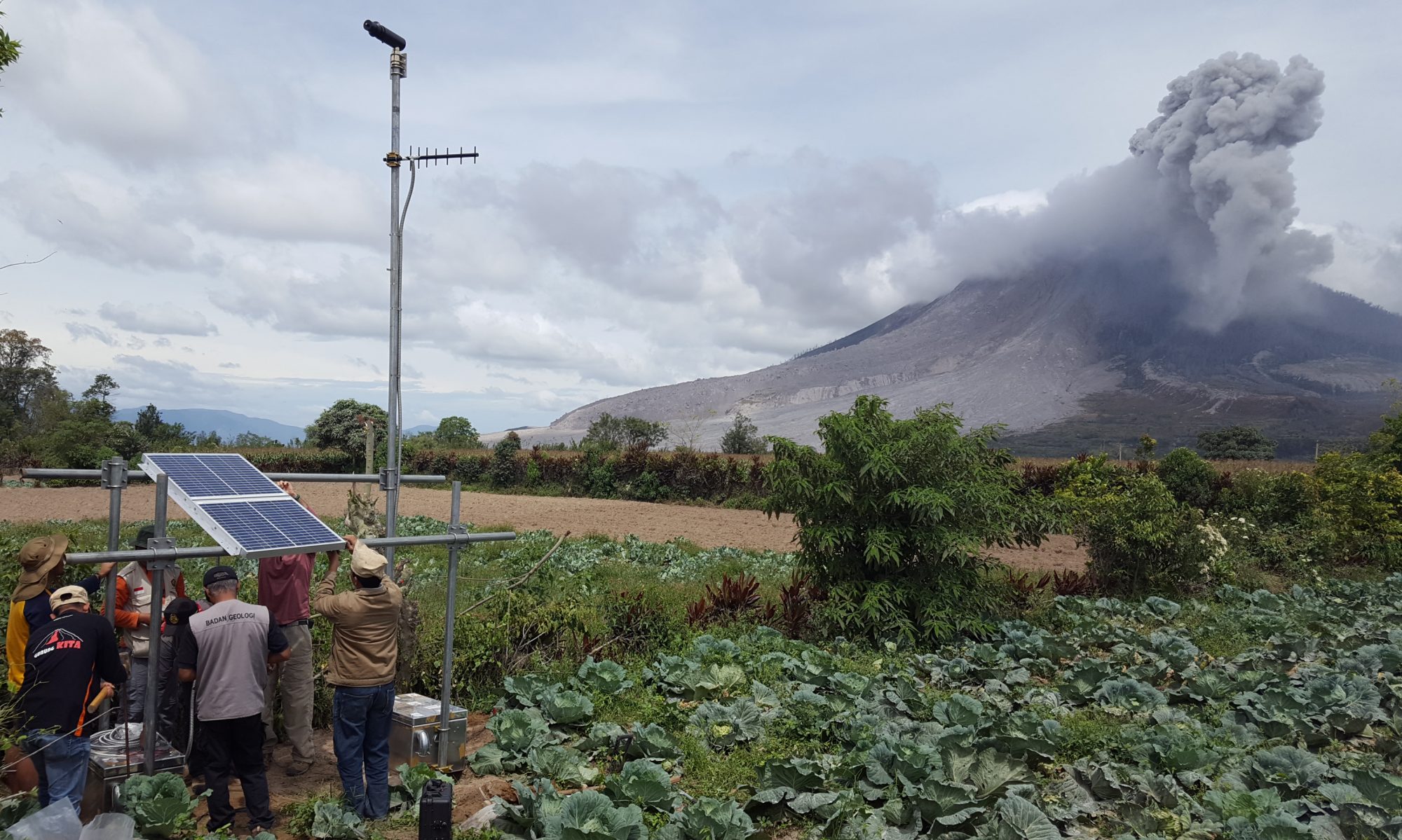
We are pleased to present a detailed database of SO2 emission rates, plume locations, and meteorological conditions, derived from measurements conducted during the period 2005-2016 at 32 volcanoes in NOVAC. The database is hosted at https://novac.chalmers.se/.
Data presented in this database indicates the magnitude and natural variability of degassing observed at a daily temporal scale.
These data are freely accessible but we expect that proper credit is given to volcano observatories in case of scientific use, as indicated in our Data Use Agreement https://novac.chalmers.se/datauseagreement.
An article describing and analyzing these data was published by the collaboration: Arellano et al. (2021), https://essd.copernicus.org/articles/13/1167/2021/essd-13-1167-2021.html